Watch the video below to learn VRAY Non-Destructive Metal Analysis
Non-Destructive Metal Analysis (NDMA) operates on the fundamental principle of evaluating a material's characteristics without causing any permanent alteration or damage to the object being tested. This is crucial for maintaining the integrity of components, ensuring product lifespan, and verifying quality without sacrificing the sample. At its core, NDMA leverages various physical phenomena where an external energy source interacts with the material, and the material's unique response or interaction is measured and analyzed. For instance, X-ray Fluorescence (XRF), a prominent NDMA method, relies on atoms emitting characteristic secondary X-rays when excited by primary X-rays. The energy and intensity of these fluorescent X-rays act as a unique "fingerprint," allowing for precise identification and quantification of elements. Other principles include the use of high-frequency sound waves (in ultrasonic testing), electromagnetic fields (in eddy current and magnetic particle testing), or the thermal properties of materials (in infrared thermography). By carefully interpreting these interactions, NDMA provides vital insights into a metal's composition, structural integrity, and potential defects, all while keeping the item fully intact for its intended use. This preservation of the material is the cornerstone of NDMA's value across countless industries.
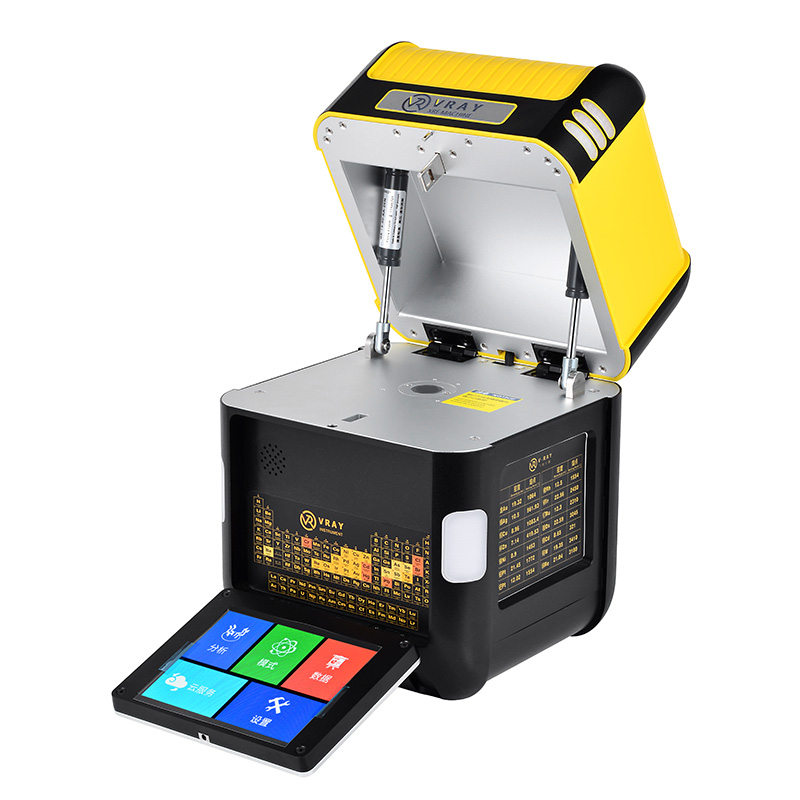
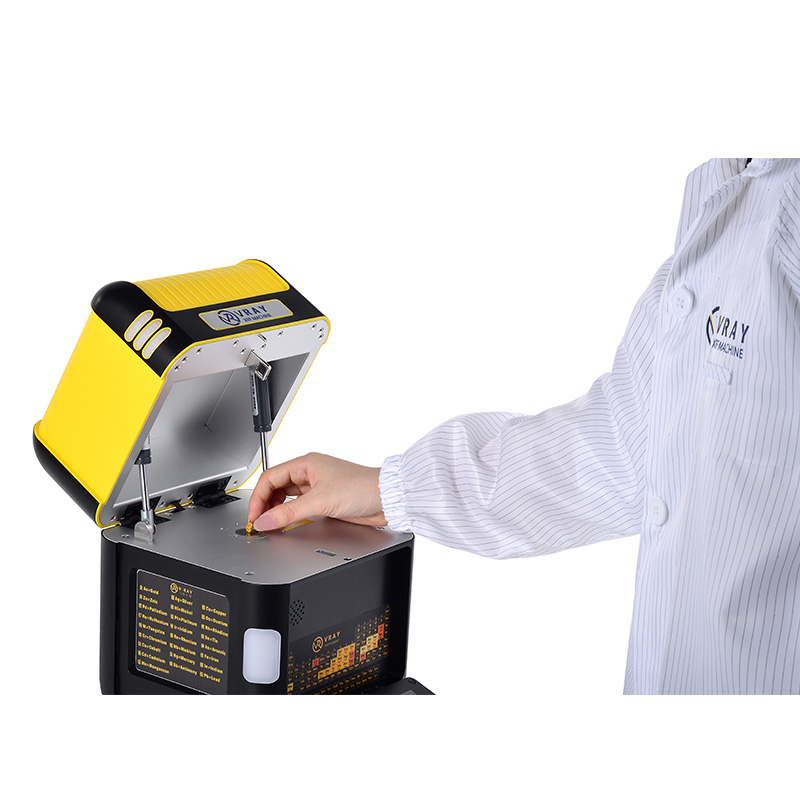
A diverse array of specialized tools are employed in Non-Destructive Metal Analysis (NDMA), each designed to harness specific physical principles for evaluation. For elemental composition analysis, XRF Analyzers (also known as XRF Spectrometers) are paramount. These instruments, ranging from Handheld XRF Analyzers (like VRAY's VR-H5 and VR-M5) to Desktop XRF Analyzers (such as VR-T7, VR-S7, VR-X5), utilize X-ray technology to identify and quantify elements without damaging the sample. Beyond XRF, other crucial NDMA tools include ultrasonic flaw detectors which emit high-frequency sound waves and measure their reflections to find internal defects and thickness variations. Eddy current testers are used for detecting surface and near-surface flaws in conductive materials by inducing eddy currents and monitoring changes in the electromagnetic field. Magnetic particle inspection equipment helps reveal surface and subsurface discontinuities in ferromagnetic materials by applying magnetic fields and observing particle accumulation. Additionally, visual inspection tools like borescopes and magnifiers are fundamental for surface examination. The selection of the appropriate tool depends entirely on the specific testing objective, the type of material, and the nature of the potential defects or properties being investigated.
The field of Non-Destructive Metal Analysis (NDMA) encompasses a variety of distinct methods, each offering unique advantages for evaluating metallic materials without causing damage. One of the most widely used methods is X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) analysis, which is highly effective for elemental composition and alloy identification, particularly for gold purity testing and precious metal analysis. This method is fast, precise, and ideal for on-the-spot material verification. Other prominent methods include Ultrasonic Testing (UT), which employs high-frequency sound waves to detect internal flaws, measure thickness, and characterize material properties. Eddy Current Testing (ECT) is a powerful electromagnetic method used to find surface and near-surface discontinuities in conductive materials, often applied for crack detection and material sorting. Magnetic Particle Testing (MT) is a reliable method for locating surface and slightly subsurface discontinuities in ferromagnetic materials. Liquid Penetrant Testing (PT) is used to reveal surface-breaking defects in non-porous materials by applying a penetrating liquid that seeps into discontinuities. Finally, Visual Testing (VT), though seemingly simple, is often the first and most fundamental method, involving direct or remote visual inspection of the material's surface for visible anomalies. The choice of method depends on the material, the type of defect sought, and the required depth of analysis.







What did our happy clients say?
VRAY's non-destructive metal analysis solutions are exceptional! The VR-S7 XRF spectrometer, with its 0.01% accuracy for 9999 gold, provides unmatched precision. This high level of accuracy in precious metal analysis is vital for our quality control. We're consistently impressed with its performance and reliability.
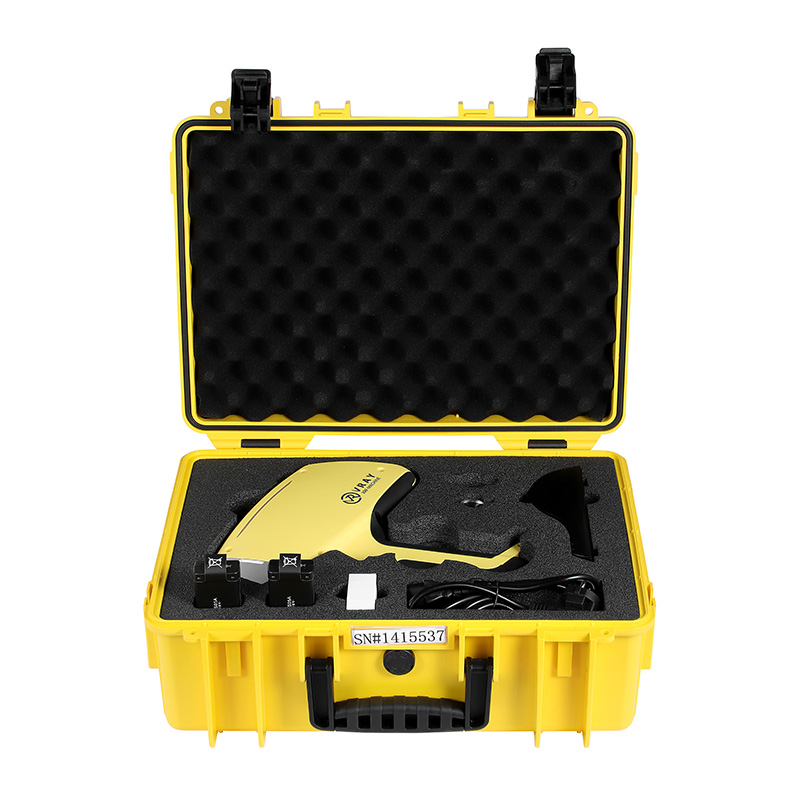
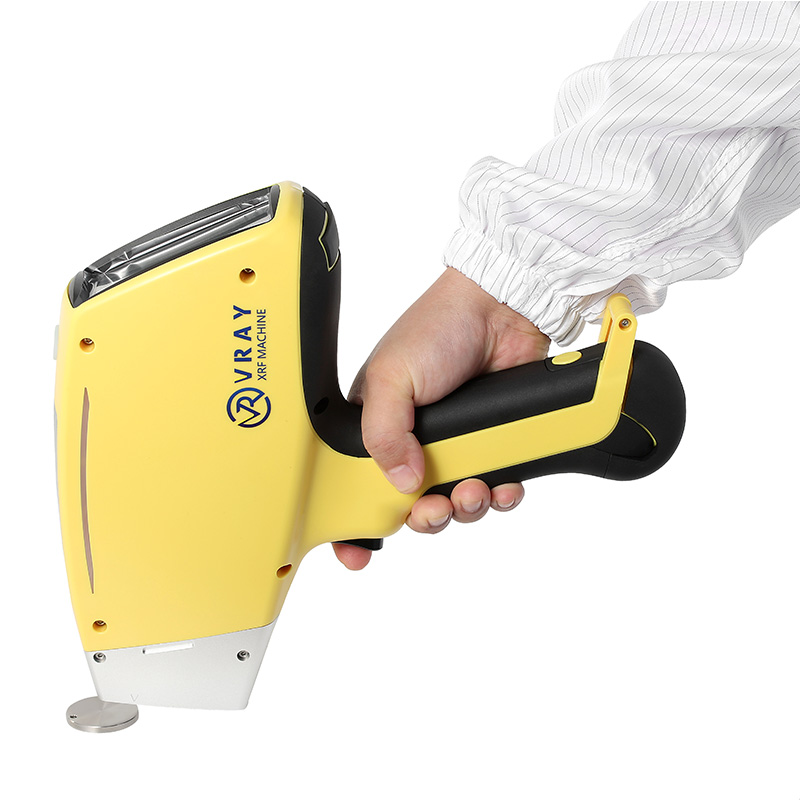
The VR-M5 portable XRF analyzer from VRAY is a game-changer for our field operations. Its 4.1kg weight combined with its robust non-destructive metal analysis capabilities makes it incredibly convenient. For $15,000-$18,000, getting such precise, on-site results is fantastic value. Highly recommended for mobile use!
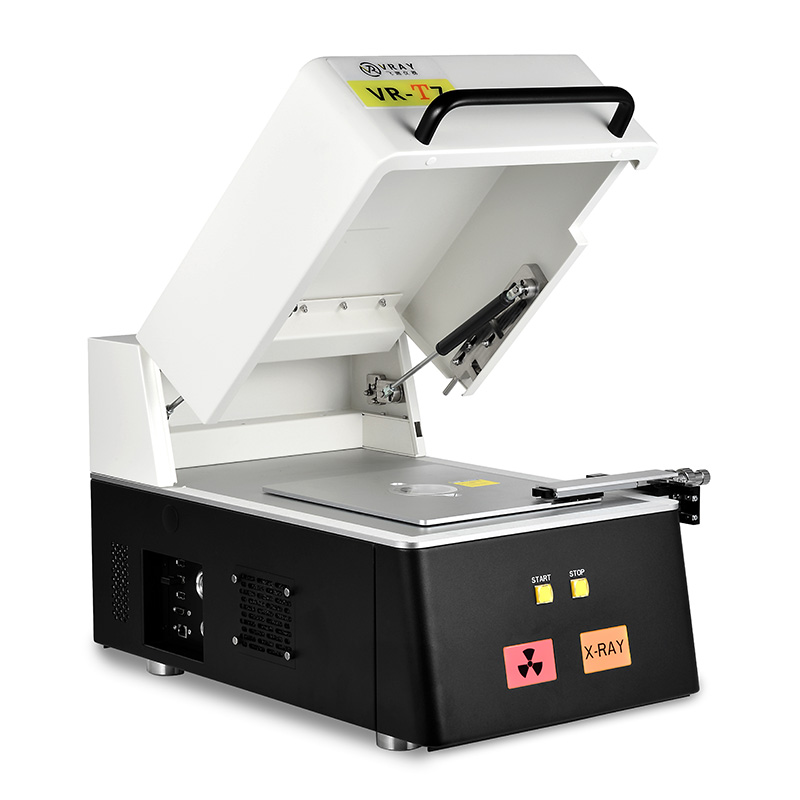
VRAY's commitment to cutting-edge XRF equipment is clear. The VR-T7 desktop gold tester offers superior detection with its SDD detector and 0.01% accuracy. This advanced non-destructive metal analysis technology ensures we always have the most reliable data. A truly professional-grade solution at a competitive price.
We found VRAY's XRF machine solutions to be incredibly cost-effective without compromising quality. The VR-X5 desktop analyzer, priced at $10,000-$11,000, offers 0.05% accuracy, which is perfect for our needs. It's a testament to VRAY's ability to provide high-accuracy non-destructive metal analysis at an accessible price point.